Cardiology Educational Information
Angiogenesis |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The development of new blood vessels | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Angiography/Coronary Angiography, or Coronary Catheterization |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A diagnostic test in which contrast dye is injected into the coronary arteries to visualize and measure the degree of coronary artery disease and vessel blockage |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Angioplasty |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A procedure in which a special catheter with an inflatable balloon at one end is used to open blocked coronary arteries; technically termed percutaneous Tran luminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) (also called balloon angioplasty) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Antianginal Agents |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The drugs that help reduce the number and severity of angina attacks, by either dilating or widening the arteries so that more blood can flow to the heart, or by reducing the heart's demand for oxygen |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Aorta |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The main artery in the body |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Arrhythmia |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
An irregularity of the heartbeat |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Arteries |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The blood vessels that carry blood from the heart to the rest of the body |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Arteriosclerosis |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The build-up of fatty deposits (plaque) in blood vessels, leading to the gradual narrowing of those vessels and restricted blood flow |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Atherectomy |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A procedure in which special cutting or grinding tools scrape plaque build-up around the artery walls |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Atherosclerosis |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A type of arteriosclerosis in which the vessels that supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart become clogged with plaque, a fatty substance, and calcium, depriving the heart muscle of the oxygen it needs for normal functioning |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cardiac Catheterization |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A procedure using special tubing (catheters) to study the heart's chambers and vessels |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Congestive Heart Failure |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A common form of heart failure that causes fluid retention leading to congestion in the lungs and edema, especially in the legs and feet |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Coronary Arteries |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Arteries supplying blood to the muscular walls of the heart |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery (CABG) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Surgery to repair or replace blocked arteries and improve blood supply to the heart muscle; commonly known as bypass surgery, it involves the use of a vein (usually from the leg), or a chest artery to form a bridge to bring blood beyond the obstruction of the affected coronary artery |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) or coronary artery disease (CHD) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The narrowing of the coronary arteries sufficiently to prevent adequate blood supply to the heart muscle; usually caused by atherosclerosis, and may progress to the point where the heart muscle is damaged due to lack of blood supply |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Diffuse Disease |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Denotes blockage throughout several sites in a coronary artery |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
End-Stage Coronary Artery Disease |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Coronary artery disease for which drugs remain the only treatment option; characterized by unrelenting angina pain, severely restricted lifestyle; see also coronary artery disease |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Heart-Lung Machine |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A mechanical pump that maintains circulation during heart surgery by shunting blood away from the heart, oxygenating it, and returning it to the body |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Heart Failure |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A syndrome in which the heart isn't able to pump enough blood to meet the demands of the body |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Hypertension |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
High blood pressure |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ischemia |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Deficiency of oxygen in a tissue due to obstruction of a blood vessel, temporary damage to living cells due to insufficient blood supply |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ischemic Heart Disease |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Another name for coronary artery disease or coronary hear disease caused by narrowing of the coronary arteries and decreased blood flow to the heart |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Myocardial Infarction |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Death of the heart muscle due to insufficient blood supply, usually due to clot obstructing blood flow (lay term: heart attack) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Myocardial Ischemia |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Decreased blood flow to the heart caused by constriction or obstruction of an artery |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Non-Invasive Procedure |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A procedure in which instruments do not enter the body (e.g. an electrocardiogram or echocardiogram) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Percutaneous |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pertains to any medical procedure where access to inner organs or other tissue is done via needle-puncture of the skin, rather than by using an "open" approach where inner organs or tissue are exposed |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Percutaneous Myocardial Channelling (PMC) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A percutaneous version of TMR performed under local anaesthesia by a cardiologist in a cardiac catheterization laboratory. Under investigation in the US, it is hoped PMC will provide the same degree of angina pain relief as the surgical versions of TMR. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
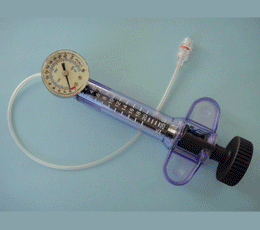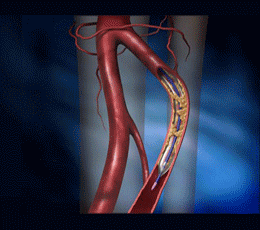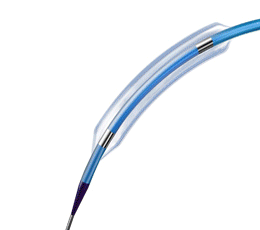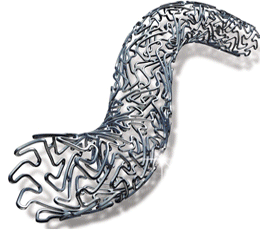
Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA or balloon angioplasty) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A non-invasive procedure in which a catheter (a thin, flexible tube) with a deflated balloon at the tip is manoeuvred into a narrow artery and inflated to open a blocked artery and allow more blood to reach the heart muscle |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Revascularization |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Establishes blood flow again to previously restricted regions of the heart |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Small-Vessel Disease |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Denotes blockage in arteries which are unusually small; frequently seen in women, persons of small stature and diabetics |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stent |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A tube inserted into an abnormally narrowed or closed artery that serves to keep the artery open and maintain flow |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Thrombus |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Blood clot |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Transmyocardial Revascularization (TMR) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A therapeutic medical laser product in by which cannels are created into oxygen-deprived heart muscle to ease angina pain and stimulate new blood vessel growth |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||